Magneto Hydrodynamic Propulsion
Introduction
Until now there have been innumerable advances made in the technology used for propelling and improving the efficiency of a sea going vessel. From diesel power to solar energy, each one of them has seen a drastic change in the way it is being used for propelling a vessel. However, there is one more technology that holds great potential that has not been exploited fully for propelling ships – magnetic power.
Today, magnetic power is known as one of the most promising technologies for a ship propulsion system. Called magneto hydrodynamics, this unique technology helps in moving a vessel using the power of magnetism. For those who have seen the movie “The Hunt for Red October” must have heard about the technology, which is also famously known as “caterpillar drive”. The system enables a special interaction between water and magnetic field which allows the magneto hydrodynamics ship to move forward. Let’s take a closer look as to how this is done.
Construction
Those who are familiar with the term “caterpillar drive” must be aware that the technology was supposedly used to make a noiseless submarine in the movie “The Hunt for Red October”. It is believed that magneto hydrodynamics technology allows the submarine to move through the water without making significant noise. The ship propelled by magnetic power uses a special type of engine known as magneto hydrodynamics engine or MHD engine. As mentioned earlier, MHD engines are more efficient and much quieter than the conventional engines. Moreover, these engines neither have any moving parts nor a propeller attached to them.
MHD craft are made with a streamlined design for both allowing the MHD engines to run efficiently and facilitating least resistance to the craft from water. The craft’s design consists of a chamber at the bottom known as the Thruster Tube. The thruster tube is the main part of the craft, and it takes the water from front and pumps it out from the back.
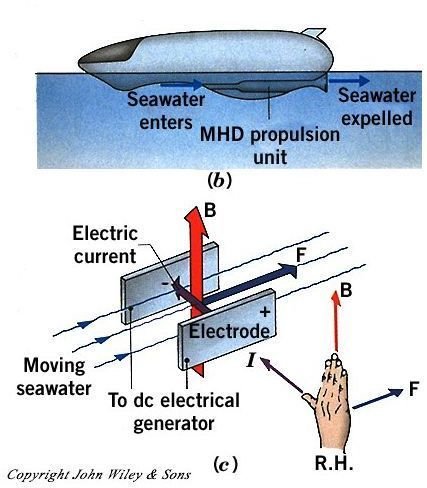
Working
As the sea water enters the thruster tube at the forward, an electric current and a magnetic field are passed through the tube. The electric current and the magnetic field both act at right angles to each other and flow in the direction of the water current. The salt present in the sea water makes it conduct electricity and the sea water thus interacts with the electric and magnetic fields in such a way that the water is pushed out from the back of the craft with full force. As the sea water forces out from behind, the vehicle accelerates in the forward direction. The thruster tube keeps sucking in the water continuously from the forward end and pumps it out at higher speed from the back, providing a constant speed to the craft.
Additional Information
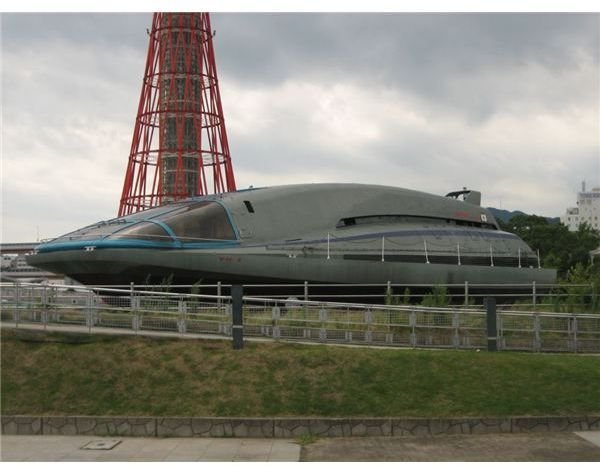
The first MHD engine was used in 1992 and it was then that it received world wide attention. The engine was fitted on a Japanese ship called Yamato1, which consisted of two MHD engines and didn’t have any moving parts.
However, the problem with MHD technology is that it is more expensive than the conventional crafts and is also much slower in speed than the usual propeller engines. Moreover, comparing to the speed output, the size of the engine is much larger, which creates problem in the designing process.
