Marine Diesel Engines
Construction Materials used in Marine Diesel Engines
Construction Materials used in Marine Diesel Engines
All metals used for engineering purposes are classified in two categories.
- Ferrous metals (mainly iron) such as cast iron, wrought iron, and different forms of steels
- Non-ferrous metals (rarely iron) such as aluminum, copper, zinc, lead, and tin, etc.
Construction Materials for Marine Diesel Engines:
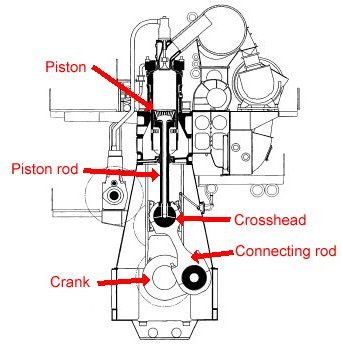
Engine Parts
1. Bed Plate:
The bed plate provides the rigid seating of the crankshaft, which is absolutely essential for satisfactory engine operation. The bed plate is constructed of a deep longitudinal girder (running along the length of engine) and transverse girder or cross girder (running across the engine). The transverse and longitudinal girders are joined together by welding.
They are made up of:
- Transverse Girder - Cast iron
- Longitudinal Girder - Mild steel
2. Frame:
Frames are provided for supporting the engine mountings, and an individual frame is fitted to each cross girder. Frames are made up of Mild Steel Plates and Tubes.
3. Holding Down:
The engine bed plate is supported on a series of chocks made up of Cast Steel / Epoxy Resin and the holding down bolts passes through the bed plate, chock, and tank top plating made up of UTS Steel.
4. Guide:
Guides are provided in the cross head assembly. They have two main parts, and they are made up of the following materials:
- Guide Bar -Mild Steel / Cast Iron
- Guide shoe- White Metal Lined
Engine Parts


5. Cylinder Parts:
Cylinder Liner:
Material: Pearlitic Grey Cast Iron
Properties of Cylinder Liner Material:
- Material for liners must provide adequate strength and fatigue life.
- Resist abrasion and corrosion and must readily transfer heat.
- Be able to retain a film of lubricating oil on working surfaces.
- Have a rate of thermal expansion compatible with adjacent parts.
To meet these requirements, liners are cast in pearlitic grey cast irons to which alloying elements such as vanadium and titanium are added to enhance strength, wear, and corrosion resistance. Chrome plated liners have extended life, but the initial cost is higher.
Chrome plated piston ring must not be used with chromium plated liners.
Cylinder cover:
Material: Pearlitic or Nodular Graphite cast Iron / Cast Steel.
Properties:
- Must be of sufficient strength to withstand the gas load at maximum pressure.
- Resist bending and be symmetrical in shape.
- Have a rate of thermal expansion compatible with adjacent parts and transfer heat readily.
Cylinder head bolt- High UTS Steel
Tie bolt - High UTS Steel
6. Piston Parts:
Piston has different parts and they are made up of following materials:
Piston:
- Piston crown - Chrome Molybdenum Steel / Nickel Chrome Steel
- Piston Skirt - Cast Iron
- Piston Rings - Cast Iron / Ordinary Grey Cast Iron
- Piston Rod - Cast Steel
- Wear Ring - (Lead-Bronze)
Materials used for piston required similar properties to those for cylinder liners and cylinder covers.
Properties of Piston Crown material:
- High mechanical strength to withstand high gas load.
- Long fatigue life to survive the fluctuating mechanical and thermal stress.
- High thermal conductivity and low co-efficient of expansion.
- High surface property i.e. hardness, anti-corrosive.
- The metal must resist high temperature creep, corrosion and erosion.
Properties of Piston Ring material:
- Highly mechanical strength and good tension properties.
- Elasticity and wear resistance with low-friction.
- Must be corrosion resistance with low- friction.
- Must be corrosion resistance and resistance against high temperature.
- Self lubricating properties.
- Must readily transfer heat and compatible with cylinder material.
- Compatible with piston for thermal expansion to maintain ring groove clearances.
Piston

7. Crankshaft
Materials: These are some of the commonly used materials to build the crank shaft.
- Low alloyed Cr –Mo steel which has tensile strength (590-680) N/mm2
- Unalloyed Carbon Steel (Normalized).
- Mild Steel (Cast throw).
- Carbon Steel (forged or cast).
- Nickel steel (forged).
Properties of Crank Shaft materials:
- Besides strength, the material should have a high endurance limit to fatigue failure.
- The material should be capable of good surface finish.
- Must be hardened to resist wear of journals and crank pins.
- Must be tough to carry load.
- Must be rigid to resist bending of the shafts.
- But it should confirm bearing line alignment.
8. Exhaust Valve
8. Exhaust Valve
The exhaust valves are made up of following materials:
Exhaust valve:
- Spindle - Nimonic Material
- Lid - Nimonic Material
- Seat - Stellite Material
- Cage - Pearlitic Cast Iron
- Guide - Pearlitic Cast Iron
- Bush - Bronze
9. Stuffing Box
- Upper Rings - Bronze Alloy
- Lower Rings - Cast Iron Alloy
10. Camshaft- Steel Alloy with Hardened surface
11. Connecting rod bolt- High UTS Alloy Steel
12. Bearing- White metal Alloy
Image Credit:
https://www.emma-maersk.com/engine/Wartsila_Sulzer_RTA96-C.htm