Universal Motors - Learn about motors that can operate on both single phase AC and DC supply
Introduction
We have been talking about various types of electrical motors, such as single phase motors, self starting induction motors, slip ring motors to name a few. In this article we will talk about a unique type of motor known as universal motor.
A motor which may be operated (or) which can run on either a direct supply or a single phase ac supply is known as universal motor.
Why it is called as a universal motor? It is because of its ability to run on both AC and DC supply with almost similar characteristics.
A universal motor has a high starting torque and variable speed characteristics. Such motor runs at dangerously high speeds during no load period.
Types
A universal motor can be manufactured in two different ways.
· Non-compensated type with concentrated poles
· Compensated type with distributed field.
The compensated type is preferred for high power rating appliances and the Non-compensated for low power rated appliances. Both the compensated and Non-compensated have construction similar to that of a DC series motor.
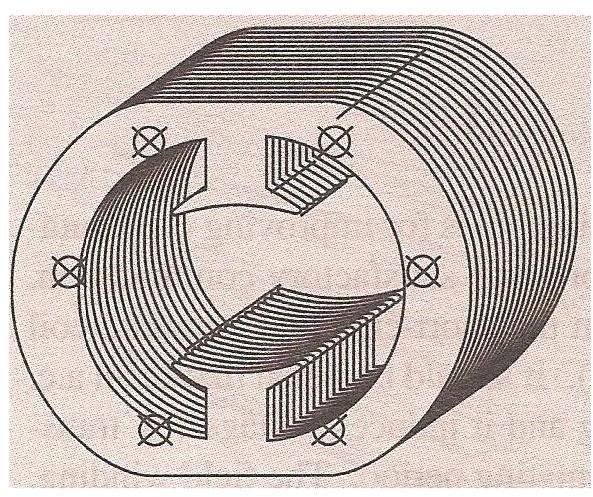
Non-Compensated motor
The Non-compensated motor has 2 salient poles and it is laminated. The armature is of wound type and the laminated core is either straight or skewed slots. The leads of the armature winding are connected to the commutator. High resistance brushes are used along with this type of motor to help better commutation.
The skew in the armature slots serves for two purposes:
· It reduces the magnetic hum.
· It aids in reducing the locking tendency of rotor, which is called magnetic locking. Magnetic locking is a condition during which the rotor teeth remains locked under the stator teeth due to magnetic attraction between the stator and rotor. This will be considerably reduced by using the Skew
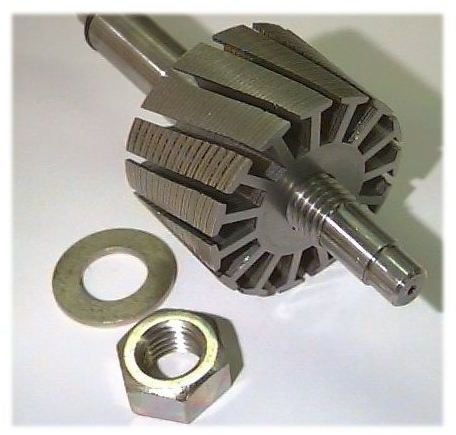

Compensated type motor
The compensated type motor consists of distributed field winding and the stator core is similar to that of split-phase motor. We already know that split phase motors consist of an auxiliary winding in addition to main winding. Similar to the split phase motors, the compensated type also consists of an additional winding. The compensating winding helps in reducing the reactance voltage which is caused due to alternating flux, when the motor runs with the aid of an AC supply.
Both the types of motors develop unidirectional torque regardless of the supply with which they run. The supply may be AC or DC but the direction of torque is same.
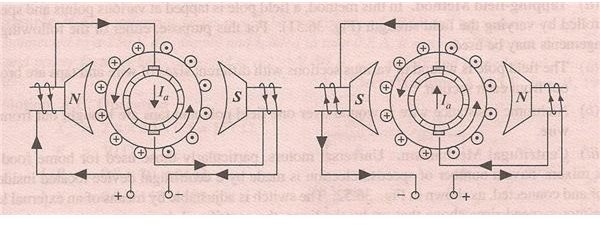
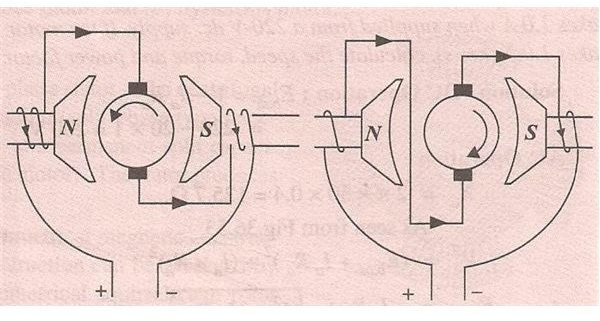
Can the direction of rotation be reversed for these types of motors?
Yes. The direction of rotation can be changed. For the non-compensated motor having salient pole, the direction of rotation can be reversed by changing the direction of flow of current through the armature or field winding. This can also be done by interchanging the leads on the brush holders.
In case of compensated type motor, either the armature leads or the field leads and shifting the brushes against the direction of rotation of motor. This helps in reversal of rotation.
Speed/Load characteristics and Speed Control
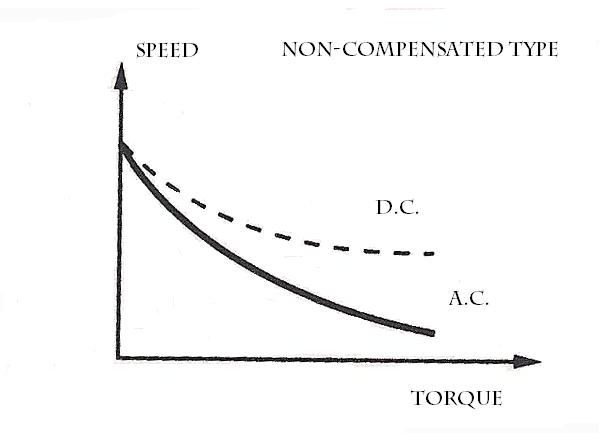
Speed/Load Characteristics:
Very similar to that of DC series motor, the universal motor also has varying speed characteristics. The speed is low at full loads. The speed is Very high and dangerous at no-loads. During no-loads the speed is limited only by its own frictional and windage load.
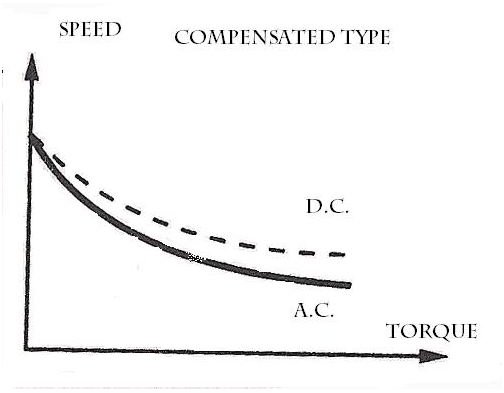
Speed control:
Speed control of universal motor is very important and the following methods are employed for the speed control of universal motors.
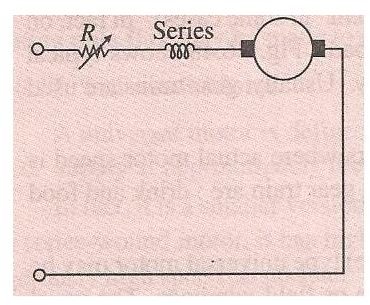
Resistance method:
In this method of speed control a variable resistance is connected in series with the motor. The amount of resistance in the circuit can be changed. A foot pedal is used for this purpose. Usually this method is employed for motors used in sewing machines.
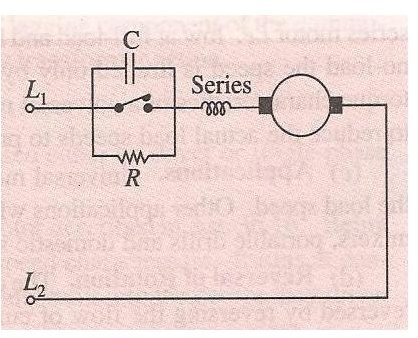
Centrifugal Mechanism:
This method is involved whenever the application involves a number of speeds. Best example is home food and fruit mixers. Here a centrifugal device is attached to the motor. If the motor rises above the specified speed set by the lever, the centrifugal device opens the contact and R comes in contact with the circuit. This causes the motor speed to decrease below the set speed. When the motor runs slower than the speed set by the lever, the contact is established and resistance is short circuited. This causes the speed to increase. The variations in speed are noticeable as the process is repeated in a rapid manner.
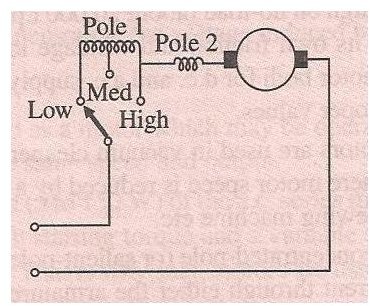
Tapping-Field Method:
As the name suggests the field is tapped at various points in this method. This is done by wounding the field pole.
Now how this tapping arrangement is established?
The tapping arrangement is established by two ways
· The various sections in the field pole are wounded and different sizes of wire and taps are brought out from those sections.
· In the second method, resistance made of Nichrome is wounded over the field pole. Various tappings are brought out from this wire.
Applications
Universal motors are mostly employed in
· Vacuum cleaners
· Portable drills
· Drink mixers
· Sewing machine
Picture and Content Courtesy:
Engelmann, R.H. & Middendort, W.H. (1994) Handbook of Electric Motors. New York: Marcel Dekker
“www.ewh.ieee.org”