How do you get Electricity from a Lemon? Making Electricity from Lemon
Introduction
Every one of us is familiar with the school experiment involving a lemon conducting electricity. This 5th grader experiment, though simple, still arouses curiosity in people of all ages. However, there are many who still don’t know as to how and why electricity is produced from a lemon. In this article we will try to unravel the mystery once and for all.
Understanding the Basics
All of us know how an electro-chemical battery works. The construction and working of the lemon experiment can be compared to a conventional battery having electrodes and electrolyte. “Lemon battery”, as the experiment is popularly known, requires two external metal electrodes in the same way; however the electrolyte is supplied by the lemon itself.
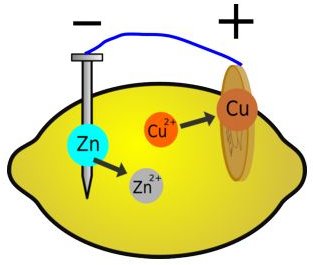
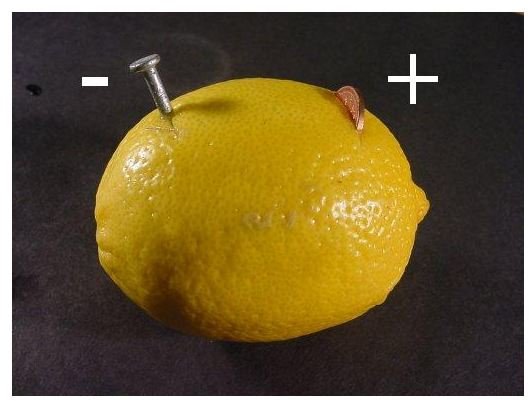
In a conventional battery, the two electrodes are two different metal pieces (Usually copper and zinc), submerged in an acidic solution (electrolyte) and connected through an external wiring to a voltmeter or a small bulb. Similarly, for a “lemon battery” experiment, two different metals in the form of a zinc nail and a copper coin are inserted into a juicy lemon. The lemon battery is also known as a voltaic battery which produces electricity by converting chemical energy to electrical energy.

How is Electricity Produced?
For understanding how electricity is produced in a lemon we will go through the basic principle of transfer of electrons and electro-chemical reactions. The juice of lemon is acidic in nature and works as a powerful electrolyte. The lemon itself serves as a reservoir for transfer of electrons to and from the electrodes. When the two electrodes, copper and zinc, are suspended in the acidic lemon juice, the atomic structure of the atoms of both the electrodes starts breaking, resulting in production of individual electrons.
Both the electrodes are not in contact with each other and thus a flow of electrons is generated through the electrodes and electrolyte. The copper acts a positive electrode and the zinc acts as the negative electrode. Both the metals are good conductors of electricity and thus a flow of electrons take place from the negative to positive electrode. This free flow of electrons results in the generation of an electric potential. Depending on this electrons flow rate, the amount of voltage generated is measured using a voltmeter. Thus this experiment proves that electricity can also be generated just by plain chemical reaction.
However, it is to note that electricity will be generated only when the battery circuit gets completed by external wiring. Also, it is not the lemon which is the source of energy, but the chemical change in the zinc that produces electricity. The zinc electrode, when inside the lemon, gets oxidized by releasing electrons and goes to a lower energy state. This leads to the transfer of electrons from a high energy state electrode to a low energy state electrode. Thus, lemon just serves as an environment for the generation of electricity; however doesn’t produce any electrons on its own.
The voltage produced by a single lemon is very small. However, a series of lemons can be used to increase the voltage of the whole battery. A series involving four lemon batteries can easily light an LED.