Basic steam generation system on a diesel ship
Introduction
The overall running of the ship should be as cost effective as possible. Various arrangements and designs are made and introduced just to make sure that ship becomes more cost effective and fuel efficient while running. All the diesel ships have a steam generation arrangement, which is fitted to prevent wastage of heat and increase the overall efficiency of the ship.
Lets’ take a look as to how the whole system of steam generation works in a diesel ship.
Exhaust Gas Heat exchangers
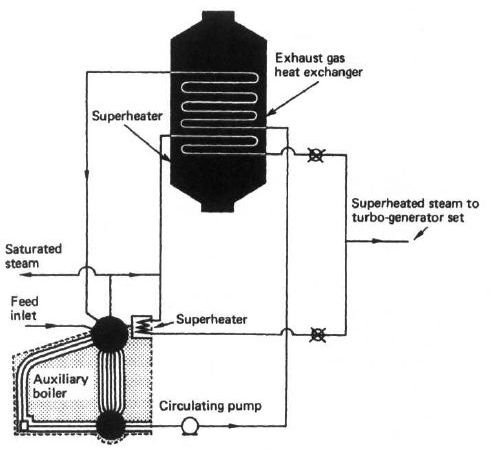
Exhaust gas heat exchangers make use of the exhaust gases from the diesel engines to produce steam. The arrangement is so made that none of the heat energy from the exhaust gases go waste. Exhaust gas heat exchangers are also known as exhaust gas boilers.
Exhaust gas boilers are not the only source for producing steam on ships having diesel engines as main propulsion systems. The ship also has conventional oil fired boilers.
The exhaust gas boiler is basically a heat exchanger with a row of tube banks, through which the feed water passes. Over these tubes hot exhaust gases are allowed to pass. Thus, just in the case of a normal heat exchanger, the heat is transferred from the hot gases to the feed water converting the later into steam. The steam generated is not fully devoid of moisture and thus special arrangements are made to superheat the steam. The source of heat energy to the superheater is also from the hot gases of the engine exhaust. The feed water is heated with the help of a pre-heater fitted in the feed line. A boiler drum is needed to continuously supply feed water, to receive steam and for the separation process. Generally, auxiliary boiler drums are used for this purpose
Auxiliary Steam Plant System
When the ship is at sea, the auxiliary boilers act as a steam receiver. This means that during sailing, only the exhaust gas boilers are used and the auxiliary boilers are shut off. Yet the auxiliary boilers’ drums are used for steam generation, separation and circulation processes for the steam generated in the exhaust boilers. When at port, the auxiliary boilers are used as normal oil fired boilers.
Thus, the auxiliary steam plant consists of an exhaust gas heat exchanger at the bottom of the funnel and one or two oil fired watertube boilers.
References
Introduction of Marine Engineering 2nd Edition by D.A Taylor
Image credits
Introduction of Marine Engineering 2nd Edition by D.A Taylor