Robots monitoring the sea for various parameters
What are Argo Floats ?
Argo Floats are special kind of autonomous robots that remain at sea for a prolonged period of time, collecting and monitoring various parameters such as temperature, salinity, velocity and similar properties of sea water. At present there are around 3000 Argo robots floating around in various oceans of the world. These robots make high quality temperature and salinity profile on the basis of data procured from the upper 2000 m ice-free layer of the global ocean currents.
Construction and Design
The structure of Argo robot is divided into three main parts :
- Hydraulics
- Microprocessors
- Data transmission system
The hydraulics system controls an inflatable internal bladder that makes the robot float or dive. The mechanism consists of a hydraulic piston which operates with the help of a batteries and a small pump. The buoyancy is controlled by the piston moving downward and inflating the hydraulic bladder.
The microprocessor controls and administers the functions of the robot. Microprocessors are pre programmed which makes the system autonomous and self reliant, though it can be controlled from a remote station.
The Data transmission system controls the communication functions with the satellite.
The whole Argo robot is approximately 25 Kg in weight and 110 cm in length, with maximum operating depth of 2000 M. The picture given below clearly shows the detailed cut out diagram on a typical argo float and the various parts have been marked very clearly on the same. Another photograph towards the right hand side shows the real picture of an argo float dropped in sea water and clearly shows how it looks from outside.
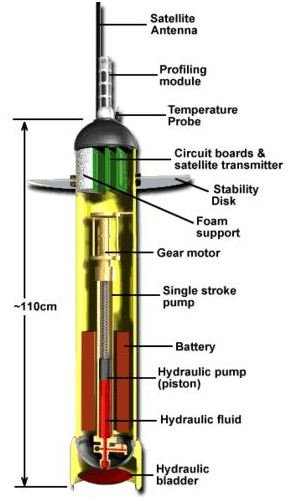

Working
On the basis of the operating region and profile requirement, the float descends to the cruising depth and drifts at that level for several days. The buoyancy is maintained at the required depth by being neutrally buoyant, i.e., to adjust the density equal to the ambient pressure and compressibility less than the sea water. Once the data is collected, the robot ascends to the surface by pumping fluid into the external bladder, in order to make salinity and temperature profiles. This completes 1 cycle. Floats are designed to make 150 such cycles. All the parameters taken at various depths such as drift depth, vertical sampling resolution and the timing are precisely recorded. This data is sent to the satellite when the robot ascends to the surface.
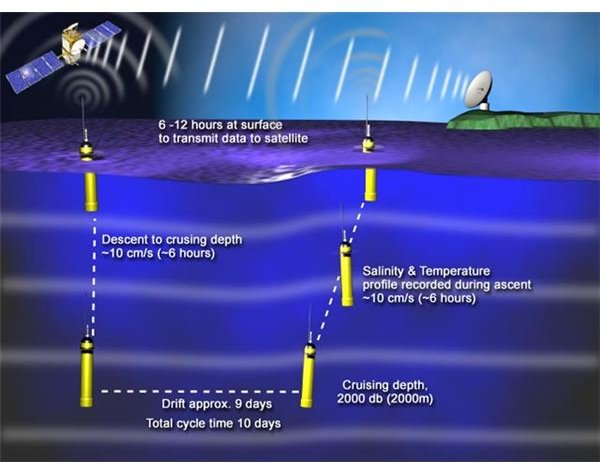
What is the need of Argo?
Ships sail at sea at the mercy of the elements and hence it is very important not only to know the immediate weather conditions but also to study long term climate and parameters of the oceans in detail. Argo robots are used to study the global changes in the ocean parameters.
It is a known fact that sea levels are rising at a rate of 3mm / year as a result of the global warming. The ice at the poles is also reducing, leading to extreme weather changes. Thus the need of Argo robots becomes more valid in order to understand and predict the changes in atmosphere and ocean parameters. Lack of such updated environmental data will make us incapable of predicting natural calamities and disasters, leading us to become victims of the same.
Image Credits
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California, USA
National Oceanography Center, Southampton, UK
NASA Earth Observatory Website
