Operation of Boiler and Conductivity in Drum Water and Feedwater
Feed water and boiler water need monitoring as any impurities in them gets concentrated and gets carried over in the steam. Conductivity has to be checked before and after the cation column, extraction pump discharge, economizer inlet, hotwell, and make-up treated water outlet. In all these places the conductivity is to be maintained within limits. Normally the range to be maintained at each area, the alarm value, and trip values are specified by the designer depending upon the pressure cycle of the plant.
- Boiler drum water before cation conductivity is maintained between 10 to 30 μS/cm
- Boiler drum water after cation conductivity is maintained between 5 to15 μS/cm
- Extraction pump discharge conductivity after cation columns is maintained between 0.1 to0.3 μS/cm with an alarm value of 0.5 μS/cm
- Economiser inlet after cation columns conductivity is maintained between 0.1 to0.3 μS/cm
- Hotwell conductivity is maintained between 2 to 4 μS/cm
- Make-up treated water outlet conductivity is maintained between 0.02 to0.1 μS/cm with alarm level at 0.2 μS/cm and trip at 0.4 μS/cm
To prevent corrosion of boiler heat transfer surface in evaporator, superheaters, reheaters, and turbine, the quality of feedwater and boiler drum water are chemically controlled. Boiler outage due to tube failures is the main concern and generally this causes long term over heating failure due to deposits. Many methods of chemical control are adopted like the all volatile treatment, the phosphate treatment, combined water treatment, etc.
The high conductivity reading at various locations gives indications about the source of the problem. If the conductivity at the make-up treated water outlet goes above 0.1 μS/cm and still keeps rising, then it is an indication that the stream in service is exhausting and needs to be taken out of service with the other mixed-bed stream brought into service before the alarm level is reached. In the case of the hot well, if the conductivity reading is below 2 μS/cm, then it is an indication of LP dosing failure. If the reading indicated is greater than 4 μS/cm, then it can be due to over-dosing of LP dosing chemicals or condenser tube leakage. At the economizer inlet if the conductivity increases, then it can be due to the cation column exhausting.
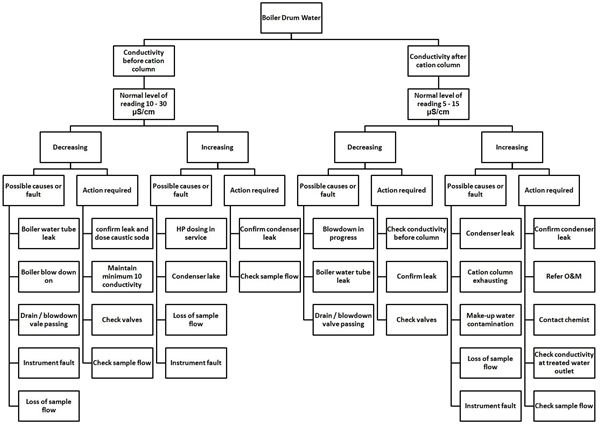
The change in conductivity in boiler drum water below or above the range before and after cation column can be due to many reasons. The probable reasons and the corrective action that can be taken are listed.
Conductivity decreasing before the cation column
Probable reasons
- Boiler water tube leakage
- Boiler blowdown is in progress
- Boiler drain valves or blowdown valves passing
- Instrument reading wrongly due to fault or loss of sample flow
The corrective action
- Confirm tube leak and dose caustic soda through HP dosing system and maintain conductivity
- Check drain valves and blowdown valves for any leak and attend
- Check for free flow of sample or rectify instrument if needed
Conductivity increasing before the cation column
Probable reasons
- Condenser tube leakage
- Boiler HP dosing is in progress
- Instrument reading wrongly due to fault or loss of sample flow
The corrective action
- Confirm condenser tube leak and take action to maintain conductivity till shutting down unit
- Check for free flow of sample or rectify instrument if needed
Conductivity decreasing after the cation column
Probable reasons
- Boiler water tube leakage
- Boiler blowdown is in progress
- Boiler drain valves or blowdown valves passing
The corrective action
- Confirm tube leak, check conductivity before cation column and dose caustic soda through HP dosing system and maintain conductivity
- Check drain valves and blowdown valves for any leak and attend
Conductivity increasing after the cation column
Probable reasons
- Condenser tube leakage
- Cation column getting exhausted / exhausted
- Contamination of make-up water from the water treatment plant
- Instrument reading wrongly due to fault or loss of sample flow
The corrective action
- Confirm condenser tube leak and take action to maintain conductivity till shutting down unit
- Inform chemist regarding increase in conductivity after checking other possible causes
- Ensure mixed bed and final treated water outlet conductivity
- Check for free flow of sample or rectify instrument if needed