Understand Why Furnace Size Varies for Gas, Oil and Coal Firing
Boilers designed to generate steam for both industrial and power generation applications use fuels like coal, oil and gas. Fuel characteristics have a great impact on boiler design. The furnace designed in a boiler must be so sized that the furnace outlet temperature is predicted and achieved within reasonable limits. The furnace outlet temperature is the basis for further heat transfer surface design. It is seen that the furnace size varies considerably between coal fired boilers and oil and gas. The variation between oil and gas fired boiler furnace size is to a smaller extent only.
Design criteria for boilers
To understand why the furnace size varies between different fuels, we have to have a broad idea about the design criteria for boilers.
- First we should know the energy input level, this will depend on steam flow, feed water temperature, pressure and temperature of steam, and an assumed efficiency of boiler based on experience.
- The energy absorption level needed in boiler and other heat transfer system will have to be defined or worked out.
- Based on the fuel given, for design calculate the fuel quantity, air and flue gas flow required.
- Now determine the size and shape of furnace which will require knowledge of burner size, other combustion systems, emission requirements, ash handling, furnace outlet temperature limitation, etc.
- Design superheaters, reheaters, ecomomisers, and air heaters so that the second pass can be finalized. Care must be taken to size the heat transfer areas such that any requirement due to fouling and the erosive nature of fuel is addressed.
- Design the desuperheating requirement, location and number of equipment for cleaning of pressure parts.
- Boiler enclosures, supports, piping, expansion guides, and movements are all to be designed and checked.
- The code to which the boiler is designed is very important and has to be adhered.
Coal fired boiler furnace
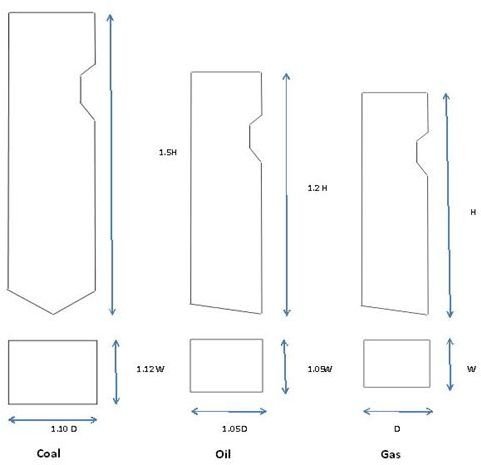
The coal fired boiler furnace size is generally higher in volume by 20 to 35 %, depending on coal types, when compared to an oil fired boiler. The factors that increase the furnace size are many.
- The reactivity of coal is much lower than oil and hence need more residence time.
- Even though the adiabatic flame temperature is higher than oil, the practically obtained flame temperature is much lower around 1700 degree Celsius.
- The lower flame temperature needs more radiant surface to be provided.
- The ash in coal needs to be addressed and hence the rule of thumb is to keep the furnace outlet temperature lower than initial deformation temperature of ash by 50 degree Celsius.
- The ash deposits on the walls reduce the effectiveness of heat transfer and this is lower in the case of coal fired boilers.
- As it is not possible to have an accurate analytical solution for heat transfer in a steam generator furnace, this leads to conservative sizing by designers.
- There are three furnace heat loading adopted by designers, the EPRS (Effective Projected Radiant Surface), the plan area and the volumetric. By virtue of experience and field results from boilers, these loadings are much lower for coal fired boilers.
- Being a solid fuel, the burner size and numbers go up when compared to oil or gas burners; this factor also influence the furnace size to the higher side.
- The bottom ash handling requirement increase the size of coal fired boiler. Normally about 20 % ash is collected as bottom ash in coal fired boiler. The oil and gas fired boilers have nearly flat furnace bottoms.
It is to be remembered that among coal fired boilers themselves, the furnace sizes will vary considerably depending on the age of the coal, ash characteristics, the reactivity, etc.
Oil fired boiler furnace
Oil flame emissivity is higher than coal flame and so results in higher furnace absorption. The furnace heat loadings can also be maintained much higher due to near zero % ash. The very low % of oil ash needs to be addressed from point of view of high temperature corrosion in heat transfer surface. As a very general rule the volume of oil fired boiler furnace will have only 65 % of volume of a coal fired boiler furnace.
Gas fired boiler furnace
When compared to oil, gas is a much more reactive and cleaner fuel. This allows still higher heat loadings in the furnace, higher second pass gas velocity, etc. All these factors reduce the furnace size further and result in the lowest furnace size for a similar capacity boiler.
Just to give an idea, a size comparison between coal, oil and gas fired boiler furnace is shown. This is a very rough comparison and is for a specific nature of coal.