What is Dehumidification? Cooling & Dehumidification, Heating & Dehumidification
What is Dehumidification?
The process in which the moisture or water vapor or the humidity is removed from the air keeping its dry bulb (DB) temperature constant is called as the dehumidification process. This process is represented by a straight vertical line on the psychrometric chart starting from the initial value of relative humidity, extending downwards and ending at the final value of the relative humidity. Like the pure humidification process, in actual practice the pure dehumidification process is not possible, since the dehumidification is always accompanied by cooling or heating of the air. Dehumidification process along with cooling or heating is used in number of air conditioning applications. Let us see how these processes are obtained and how they are represented on the psychrometric chart.
This article describes psychrometric processes like dehumidification, cooling and dehumidification, and heating and dehumidification. The article describes how these processes are achieved and how they are represented on the psychrometric chart.
Cooling and Dehumidification Process
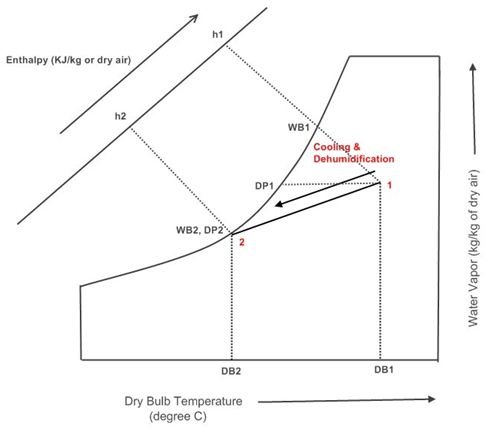
The process in which the air is cooled sensibly and at the same time the moisture is removed from it is called as cooling and dehumidification process. Cooling and dehumidification process is obtained when the air at the given dry bulb and dew point (DP) temperature is cooled below the dew point temperature.
Let us understand the cooling and dehumidification process in more details. When the air comes in contact with the cooling coil that is maintained at the temperature below its dew point temperature, its DB temperature starts reducing. The process of cooling continues and at some point it reaches the value of dew point temperature of the air. At this point the water vapor within the air starts getting converted into the dew particles due to which the dew is formed on the surface of the cooling and the moisture content of the air reduces thereby reducing its humidity level. Thus when the air is cooled below its dew point temperature, there is cooling as well as dehumidification of air.
The cooling and dehumidification process is most widely used air conditioning application. It is used in all types of window, split, packaged and central air conditioning systems for producing the comfort conditions inside the space to be cooled. In the window and split air conditioners the evaporator coil or cooling coil is maintained at temperature lower than the dew point temperature of the room air or the atmospheric air by the cool refrigerant passing through it. When the room air passes over this coil its DB temperature reduces and at the same time moisture is also removed since the air is cooled below its DP temperature. The dew formed on the cooling coil is removed out by small tubing. In the central air conditioning systems the cooling coil is cooled by the refrigerant or the chilled water. When the room air passes over this coil, it gets cooled and dehumidified.
In the general the cooling and dehumidification process is obtained by passing the air over coil through which the cool refrigerant, chilled water or cooled gas is passed.
During the cooling and dehumidification process the dry bulb, wet bulb and the dew point temperature of air reduces. Similarly, the sensible heat and the latent heat of the air also reduce leading to overall reduction in the enthalpy of the air. The cooling and dehumidification process is represented by a straight angular line on the psychrometric chart. The line starts from the given value of the DB temperature and extends downwards towards left.
Heating and Dehumidification Process
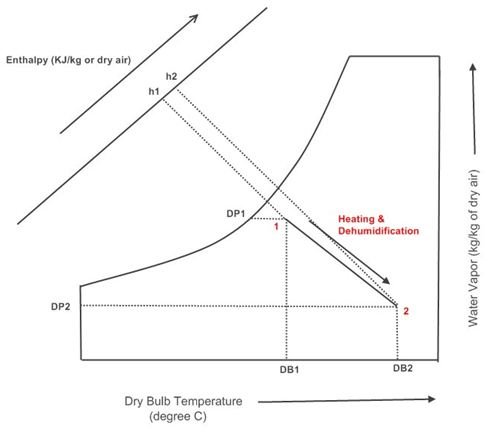
The process in which the air is heated and at the same time moisture is removed from it is called as heating and dehumidification process. This process is obtained by passing the air over certain chemicals like alumina and molecular sieves. These elements have inherent properties due to which they keep on releasing the heat and also have the tendency to absorb the moisture. These are called as the hygroscopic chemicals.
In actual practice the hygroscopic elements are enclosed in the large vessel and the high pressure air is passed inside the vessel through one opening. When the air comes in contact with the chemicals the moisture from the air is absorbed and since the chemicals emit heat, the DB temperature of the air increases. The hot and dehumidified air comes out from the vessel through other opening in the vessel. The inlet and outlet openings of the vessel are controlled by the valve.
The heating and humidification process is commonly used for reducing the dew point temperature of air. There are number of automatic valves in the chemical plants that are operated by the compressed air at high pressure. If the dew point temperature of this air is high, there are chances of formation of dew inside the valves which can lead to their corrosion and also faulty their operation. Thus it is very important that the air passing to such automatic valves have very low dew point temperature. The heating and dehumidification process by using hygroscopic materials is used often in the air drying units.
During the heating and dehumidification process dry bulb temperature of the air increases while its dew point and wet bulb temperature reduces. On the psychrometric chart, this process is represented by a straight angular line starting from the given DB temperature conditions and extending downwards towards right to the final DB temperature conditions.
This post is part of the series: Psychrometric Chart
This is the series of articles that describes psychrometric chart and various psychrometric processes like sensible heating, sensible cooling, humidification, de-dumidification, evaporative cooling etc.
- What is a Psychrometric Chart? Overview of Components
- How to Use a Psychrometric Chart
- Psychrometric Processes: Sensible Cooling and Sensible Heating of Air
- Psychrometric Processes: Cooling & Humidification and Heating & Humidification
- Psychrometric Processes: Cooling & Dehumidification and Heating & Dehumidification